In the following scenarios, you can use U-Boot instead of a Linux software update package to program the firmware in your device:
-
You only want to update one partition with the artifact generated by a Digi Embedded Yocto project.
-
You don’t have any firmware programmed in your device (except the bootloader).
-
Your bootloader is corrupt and does not boot. In this case, first see Recover your device.
| If none of these scenarios apply, Digi recommends updating the firmware from Linux. See Program firmware from Linux |
Update firmware from TFTP
U-Boot bootloader allows you to update the firmware of your device over Ethernet. U-Boot uses the TFTP protocol to get the firmware images from a TFTP server running on your computer and programs them onto the eMMC of the device.
| This update process requires a TFTP server running on your computer with a configured exposed folder. If you don’t have a running TFTP server, follow the installation instructions in Install Digi Embedded Yocto. The devices look for the firmware files in this folder when performing the update. |
Once you have the TFTP server running on your computer, you can start the update process:
-
Get the Yocto firmware images:
-
<u-boot-file>.bin for your hardware variant. See Hardware variants.
-
<boot-file>.boot.vfat
-
<recovery-file>.recovery.vfat
-
<rootfs-file>.rootfs.ext4
-
After building the Yocto firmware, you can find the image files inside the project directory at:
<project_folder>/tmp/deploy/images/<platform>
-
You can download Digi provided pre-built images from:
-
For ConnectCore 8X SBC Pro:
-
-
-
Copy the images in your TFTP server’s exposed folder (typically /tftpboot).
-
Connect the board to your host computer. See Step 2 - Set up the hardware for instructions.
-
Open a serial connection to the serial port to which the device is connected. Use the following settings:
-
Port: Serial port where your ConnectCore board is attached
-
Baud rate: 115200
-
Data Bits: 8
-
Parity: None
-
Stop Bits: 1
-
Flow control: None
-
-
Reset the device (press the Reset button on the board) and immediately press a key in the serial terminal to stop the auto-boot process. You will be stopped at the U-Boot bootloader prompt:
U-Boot dub-2020.04-r2.2 (Jan 18 2021 - 15:54:04 +0000) CPU: NXP i.MX8QXP RevB A35 at 1200 MHz at 25C DRAM: 2 GiB MCA: HW_VER=1 FW_VER=1.01 MMC: FSL_SDHC: 0, FSL_SDHC: 1 In: serial Out: serial Err: serial Model: Digi International ConnectCore 8X SBC Pro Board. ConnectCore 8X SOM variant 0x02: 2 GiB LPDDR4, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, MCA, Crypto-auth Board version 3, ID 135 Boot: MMC0 BuildInfo: - SCFW 56682d58, SECO-FW 0e4b9cee, IMX-MKIMAGE 8da5cd23, ATF c949a88 - U-Boot dub-2020.04-r2.2 flash target is MMC:0 Net: eth0: ethernet@5b040000 [PRIME], eth1: ethernet@5b050000 Fastboot: Normal Normal Boot Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0 {pu} -
Configure the network settings of the device by doing one of the following:
-
Get a dynamic IP address from a DHCP server by running the following commands:
=> setenv autoload no => dhcp -
Configure a static IP address, where a.b.c.d is the IP address of your device:
=> setenv ipaddr a.b.c.d
-
-
Configure the IP address of the machine where the TFTP server is running and save the configuration as follows, where w.x.y.z is your machine IP address where the TFTP server is running:
=> setenv serverip w.x.y.z => saveenv -
Update the U-Boot image (optional):
-
Execute the following command to update the U-Boot image:
=> update uboot tftp <u-boot-file>.bin -
Reset the board to boot into the recently updated U-Boot, and press any key to stop the autoboot process.
-
Reset the U-Boot environment to default values (this will not reset protected variables like the MAC address). To do so, issue this command:
=> env default -a -
Configure the network and TFTP settings on your device again and save the configuration.
-
-
Configure the partition of the eMMC for holding Yocto images by running these commands:
=> setenv mmcdev 0 => run partition_mmc_linux -
Update the boot image by executing this command:
=> update linux tftp <boot-file>.boot.vfat -
Update the root file system image by issuing this command:
=> update rootfs tftp <rootfs-file>.rootfs.ext4 -
Update the recovery image by executing this command:
=> update recovery tftp <recovery-file>.recovery.vfat -
You can format the update partition or directly boot the new firmware:
-
To format the update partition, run the following commands. They boot in recovery mode to format the partition and then boots the device normally with the new firmware:
=> setenv recovery_command wipe_update => saveenv => run recoverycmd -
If the update partition is already formatted or you want to preserve its contents, boot the device with the firmware you have just programmed:
=> boot
-
Update firmware from microSD
If you don’t have a TFTP server, you can still program Yocto in your device using a microSD card. The microSD card must be FAT formatted.
| Your microSD card must have at least 2 GB of capacity. |
To program Yocto from the microSD card:
-
Power off the device.
-
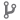
Change the boot source configuration to boot from the internal eMMC. To do so, set the boot mode micro-switches as follows:
-
BOOT.1 OFF
-
BOOT.2 OFF
-
-
Get the Yocto firmware images:
-
<u-boot-file>.bin for your hardware variant. See Hardware variants.
-
<boot-file>.boot.vfat
-
<recovery-file>.recovery.vfat
-
<rootfs-file>.rootfs.ext4
-
After building the Yocto firmware, you can find the image files inside the project directory at:
<project_folder>/tmp/deploy/images/<platform>
-
You can download Digi provided pre-built images from:
-
For ConnectCore 8X SBC Pro:
-
-
-
Place the images in the root of the FAT formatted microSD card.
-
Connect the board to your host computer. See Step 2 - Set up the hardware for instructions.
-
Open a serial connection to the serial port the device is connected to. Use the following settings:
-
Port: Serial port where the device is attached
-
Baud rate: 115200
-
Data Bits: 8
-
Parity: None
-
Stop Bits: 1
-
Flow control: None
-
-
Reset the device (press the Reset button on the board) and immediately press a key in the serial terminal to stop the auto-boot process. You will be stopped at the U-Boot bootloader prompt:
U-Boot dub-2020.04-r2.2 (Jan 18 2021 - 15:54:04 +0000) CPU: NXP i.MX8QXP RevB A35 at 1200 MHz at 25C DRAM: 2 GiB MCA: HW_VER=1 FW_VER=1.01 MMC: FSL_SDHC: 0, FSL_SDHC: 1 In: serial Out: serial Err: serial Model: Digi International ConnectCore 8X SBC Pro Board. ConnectCore 8X SOM variant 0x02: 2 GiB LPDDR4, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, MCA, Crypto-auth Board version 3, ID 135 Boot: MMC0 BuildInfo: - SCFW 56682d58, SECO-FW 0e4b9cee, IMX-MKIMAGE 8da5cd23, ATF c949a88 - U-Boot dub-2020.04-r2.2 flash target is MMC:0 Net: eth0: ethernet@5b040000 [PRIME], eth1: ethernet@5b050000 Fastboot: Normal Normal Boot Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0 {pu} -
Optional. Update the U-Boot image:
-
Execute the following command to update the U-Boot image:
=> update uboot mmc 1 fat <u-boot-file>.bin -
Reset the board to boot into the recently updated U-Boot, and press any key to stop the auto-boot process.
-
Reset the U-Boot environment to default values (this will not reset protected variables like the MAC address). To do so, issue this command:
=> env default -a -
Save the U-Boot environment to apply the default configuration.
=> saveenv
-
-
Configure the partition table of eMMC to hold Yocto images. To do so, execute these commands:
=> setenv mmcdev 0 => run partition_mmc_linux -
Update the boot image by executing this command:
=> update linux mmc 1 fat <boot-file>.boot.vfat -
Wait until the process ends, then update the root file system image by issuing this command:
=> update rootfs mmc 1 fat <rootfs-file>.rootfs.ext4 -
Wait until the process ends, then update the recovery image by executing this command:
=> update recovery mmc 1 fat <recovery-file>.recovery.vfat -
Change the default boot command in U-Boot to boot from the eMMC by issuing these commands:
=> setenv bootcmd dboot linux mmc => saveenv -
You can format the update partition or directly boot the new firmware:
-
To format the update partition, run the following commands. They boots in recovery mode to format the partition and then boots the device normally with the new firmware:
=> setenv recovery_command wipe_update => saveenv => run recoverycmd -
If the update partition is already formatted or you want to preserve its contents, boot the device with the firmware you have just programmed:
=> boot
-