What Is 5G Technology?
5G technology represents the fifth generation of mobile network connectivity, designed to dramatically improve speed, responsiveness, and capacity compared to previous generations like 4G LTE. At its core, 5G isn’t just about faster Internet — it’s a network architecture that leverages advanced radio technologies, more distributed cells, and a cloud-native core to deliver ultra-low latency, massive device connectivity, and enhanced performance for emerging applications across industries. This next-gen architecture, as explained in Digi’s blog on 5G network architecture, enables a range of transformative use cases from industrial automation and smart cities to telehealth and connected transportation by supporting higher throughput and more reliable connections in dense environments.
Top 3 Use Cases of 5G Connectivity
Whether you need faster data delivery, lower latency, or improved scalability, 5G supports your use case, as shown in the table below. You can learn more about 5G use cases and benefits in these blog posts:
| Use Case |
What It Does |
Best For |
Digi Product |
| Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) |
High-speed data (10x faster than 4G) |
Video streaming, AR/VR, cloud apps |
Digi EX50 |
| Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (uRLLC) |
Ultra-low latency (<1 ms) |
Autonomous vehicles, robotics, remote surgery |
Digi TX54 for public safety |
| Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC) |
Massive IoT connectivity (1M devices/km²) |
Smart cities, industrial sensors, asset tracking |
Digi IX40 for industrial |
Key 5G Technologies
5G NR (New Radio) uses four key technologies to deliver performance gains in speed, capacity, and responsiveness: advanced spectrum utilization, massive MIMO, beamforming, and a flexible, software-driven network architecture. Together, these technologies enable more efficient use of available spectrum, improved signal quality, and support for a wide range of high-bandwidth and low-latency applications across enterprise and industrial environments.

These standards are defined by 3GPP, ensuring global interoperability.
5G Network Architecture
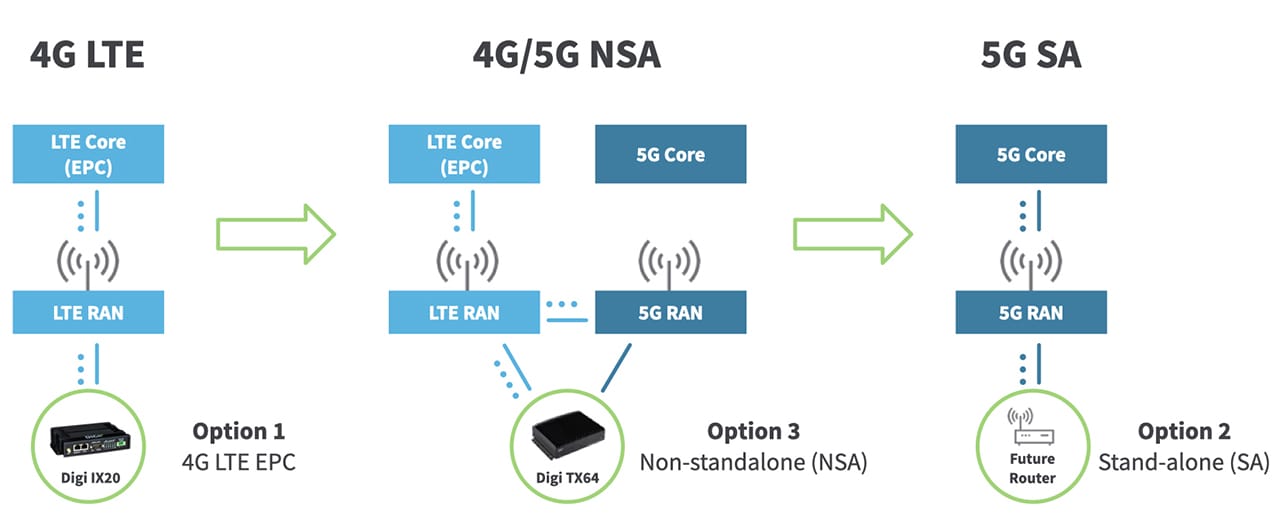
5G networks deploy in two architectures — 5G Non-Standalone (NSA) and 5G Standalone (SA). Digi cellular routers support both architectures for maximum flexibility. These deployment models define how 5G radio access integrates with the core network and play a critical role in determining performance, latency, scalability, and long-term capabilities.
5G NSA was the first architecture widely deployed, designed to accelerate time to market by building on existing 4G LTE infrastructure. In an NSA configuration, 5G New Radio (NR) is used alongside a 4G LTE core (Evolved Packet Core). This approach allows service providers to deliver higher data rates and increased capacity while minimizing initial infrastructure investment. NSA is well suited for enhanced mobile broadband use cases and early 5G adoption, but it does not fully unlock the advanced capabilities envisioned for 5G, such as ultra-low latency and extensive network customization.
5G SA represents the full realization of 5G architecture. In a standalone deployment, both the radio access network and the core network are built specifically for 5G, using a cloud-native, service-based core. This architecture enables key 5G innovations, including network slicing, edge computing integration, and support for massive machine-type communications. By decoupling network functions and running them as software-based services, SA networks provide greater flexibility, scalability, and resilience while enabling operators to tailor network behavior to specific applications or industries.
A defining feature of 5G SA is its support for network slicing, which allows a single physical network to be partitioned into multiple virtual networks, each optimized for different performance requirements. For example, one slice can prioritize ultra-reliable, low-latency communication for industrial automation, while another supports high-throughput data for video or analytics. Combined with distributed edge computing, this architecture reduces latency and improves reliability for mission-critical applications.
As organizations adopt advanced IoT, Industry 4.0, and smart infrastructure solutions, understanding 5G network architecture is essential. While NSA continues to serve as a practical bridge to 5G, SA provides the foundation for long-term innovation, enabling secure, scalable, and application-aware connectivity that meets the evolving demands of enterprise and industrial networks.
| Feature |
NSA (Non-Stand-Alone) |
SA (Stand-Alone) |
| Status |
Available now |
Rolling out gradually |
| Core Network |
Uses 4G LTE core |
Pure 5G core |
| Deployment |
Faster rollout |
Requires new infrastructure |
| Capabilities |
Enhanced data speeds |
Full 5G features (network slicing, ultra-low latency) |
| Best For |
Immediate deployment needs |
Advanced use cases and future-proofing |
- gNB (gNodeB): 5G base station
- eNB (eNodeB): 4G LTE base station (used in NSA)
- RAN: Radio Access Network connecting devices to core
- MME: Manages authentication and mobility (4G component)
- UE: User Equipment (phones, routers, modems)
5G Spectrum and Frequency Bands
5G operates across three spectrum bands with different trade-offs in coverage, capacity, and performance. These bands — low-band, mid-band, and high-band — work together to support a wide range of use cases, from broad-area connectivity to ultra-high-speed, low-latency applications. Understanding how each spectrum band functions helps organizations evaluate performance expectations and deployment options for their specific environments.
Low-band spectrum typically operates below 1 GHz and is valued for its ability to travel long distances and penetrate buildings and obstacles effectively. This makes it well suited for wide-area coverage, rural deployments, and applications that require consistent connectivity rather than extreme speeds. While low-band 5G offers improved efficiency and capacity compared to 4G LTE, its data rates are generally lower than those achieved with higher-frequency bands. As a result, low-band spectrum often serves as a foundational layer for nationwide 5G coverage and IoT connectivity.
Mid-band spectrum, commonly ranging from 1 GHz to 6 GHz, strikes a balance between coverage and performance. It delivers significantly higher data speeds and lower latency than low-band frequencies while still maintaining reasonable propagation characteristics. Mid-band 5G has become a key focus for many service providers because it supports dense urban environments, enterprise campuses, and industrial sites without requiring the extreme densification associated with high-band deployments. For many enterprise and industrial use cases, mid-band spectrum provides the optimal mix of throughput, reliability, and coverage.
High-band spectrum, also known as millimeter wave (mmWave), operates at frequencies above 24 GHz. These bands offer exceptionally high data rates, massive capacity, and ultra-low latency, enabling advanced applications such as real-time video analytics, augmented reality, and mission-critical communications. However, mmWave signals have limited range and are more susceptible to interference from physical obstacles, requiring dense deployments of small cells. As a result, high-band 5G is most effective in controlled environments like stadiums, factories, ports, and urban hotspots where performance demands are highest.
5G’s ability to leverage multiple spectrum bands simultaneously is one of its most powerful advantages. Through technologies such as carrier aggregation and dynamic spectrum sharing, networks can combine different frequencies to optimize performance based on location, device capability, and application requirements. This multi-band approach allows operators to deliver consistent connectivity while scaling capacity where and when it is needed.
For enterprises and solution providers, spectrum considerations directly impact network design, device selection, and application performance. By aligning use cases with the appropriate frequency bands, organizations can maximize the benefits of 5G, achieving the right balance of coverage, speed, and reliability to support the requirements of connected and data-driven operations.
| Band |
Frequency |
Speed |
Trade Off |
Coverage |
| Low-Band |
<2 GHz |
Similar to 4G |
Limited available spectrum means performance gains are modest compared to 4G LTE. |
Nationwide, rural, wide-area coverage |
| Mid-Band (Sub-6/FR1) |
2–6 GHz |
100s of Mbps |
Best balance between coverage range and data capacity |
Enterprise campuses, most deployments |
| High-Band (mmWave/FR2) |
24–100 GHz |
Multi-Gbps |
Requires significantly more cellular infrastructure (many small cells) to provide coverage. |
Stadiums, dense urban, fixed locations |
Most deployments use mid-band for the best balance of speed and coverage. High-band (mmWave) requires dense infrastructure and is best for fixed, high-capacity locations.
Meet Our 5G Solutions
Digi’s 5G product suite is growing! Meet the current line-up, and stay tuned for more. For customers that require the speed and low latency of 5G, Digi has multiple options today – and a roadmap for the future – whether you operate in an enterprise, industrial or mobile environment.
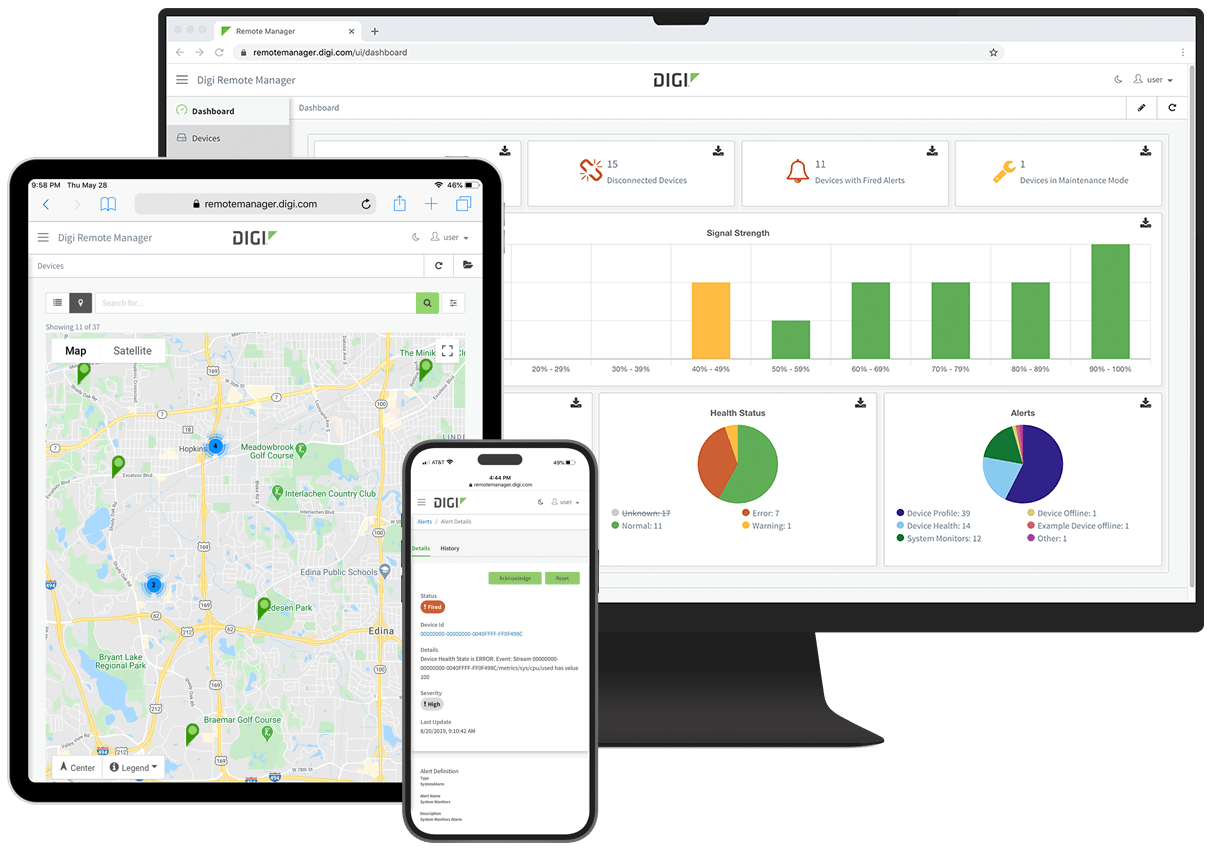 |
SOC 2 compliant Digi Remote Manager® (Digi RM) is the technology platform that brings networks to the next level, allowing networks — and the people who manage them — to work smarter. It transforms a multitude of dispersed IoT devices into a dynamic, intelligent network. Now you can easily activate, monitor and diagnose hundreds or even thousands of mission-critical devices from a single point of command. Edit configurations, update firmware, schedule and automate tasks — all from your desktop, tablet or phone. |
 |
Digi EX50 5G is a high-performance Wi-Fi 6 router with 5G/4G dual connectivity driven by industry-leading software. Digi EX50 provides businesses and managed home offices with secure, resilient, enterprise-grade connectivity for today's most demanding business environments. |
 |
Purpose-built for Industry 4.0, Digi IX40 supports the 5G connectivity and edge intelligence needed to enable numerous use cases ranging from predictive maintenance and asset monitoring to machine learning and advanced robotics. It seamlessly connects multiple machines, whether wired or wireless, in the most demanding environments, optimizing integration of cloud-delivered operational technology (OT) services with information technology (IT) to streamline complex operations and scale IT infrastructure. |
 |
An ideal and purpose-built solution for public safety and service fleets, Digi TX40 breaks down communication silos and seamlessly connects the growing list of equipment in a vehicle into a fast and reliable vehicle area network (VAN). It enables you to digitally transform your fleet with latest generation wireless technology that is affordable, easy-to-deploy and centrally managed with Digi Remote Manager. Validated for FIPS 140-2, Digi TX40 5G supports the strict requirements of government applications and public safety, and supports a range of value-added services for persistent connectivity and advanced cybersecurity. |
 |
Digi TX54 offers 5G, LTE-A Pro and LTE-A single and dual cellular models, and first responder models for critical communications, with FIPS 140-2 validation. The industrial-grade Digi TX54 cellular solution includes concurrent and independent dual cellular interfaces that prioritize critical communications, making it ideal for a range of transportation use cases, including intelligent transportation systems, smart traffic management, and emerging use cases in connected vehicle and V2X applications. As with all Digi routers, Digi TX54 is fully integrated with Digi Remote Manager for ease of deployment and ongoing management. |
 |
Digi TX64 is a high-performance, high-reliability 5G router for complex mobile deployments including transit and transportation systems — driven by state-of-the-art software for system management and security. Digi TX64 is built to handle the physical demands of mobile environments, including temperature extremes and fluctuating power. Designed for next-generation transit and fully integrated with Digi RM for remote monitoring and management, Digi TX64 supports GNSS with untethered dead reckoning (UDR) for precise positioning. It also supports FIPS 140-2 as well as value-added services for persistent connectivity and advanced cybersecurity. |
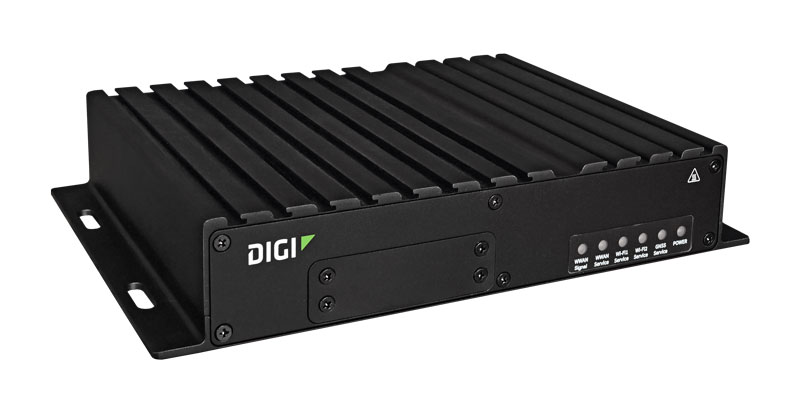 |
Digi TX64 5G Rail delivers 5G/4G/3G cellular connectivity with true enterprise class routing, security, firewall, integrated VPN and state-of-the-art software for system-wide visibility and management with Digi Remote Manager. It offers a flexible interface design with an integrated Wi-Fi access point and client, USB, serial, inertial-guided GNSS and UDR, Bluetooth® and 4-port Gigabit Ethernet switch, as well as FIPS 140-2 and a variety of configuration options and value-added services for the most robust connectivity and security. |
Fixed Wireless Access And Private 5G Networks

Wireless WAN
Cut the cord. By replacing conventional, expensive wired WANs with Digi-powered 5G wireless, you can improve performance and latency — while reducing costs and ensuring always-on resilience.

Private 5G Networks
Digi solutions are ideal for private 5G networks, connecting large numbers of devices across campuses, factories, airports, and other facilities more reliably, securely and cost-effectively than traditional approaches such as Wi-Fi.
Unlimited Possibilities
Digi 5G solutions provide performance for the latest IoT applications
Enterprise
Fixed Wireless Access
Digi 5G devices support Fixed Wireless Access for reliable connectivity anywhere, replacing older, more expensive wired connections (DSL, T1 and fiber) with a more cost-effective solution. And with 5G, you can enjoy much faster speeds and better uplink performance, resulting in a more symmetrical connection in your headquarters, your branch office or even when you’re working from home.
Cellular Failover
Digi 5G enterprise solutions work as primary or secondary connectivity for enterprise and branch office locations. 5G provides dramatically faster connections than 4G, with lower latency, resulting in a better user experience – with fast failover to prevent loss of connectivity for your business and customers.
Pop-up Stores
Wherever you may need Internet access, as well as speed and throughput, you can drop in a Digi EX50 5G cellular router and get instant connectivity, security, and reliable performance to support your retail needs, from displays to interactive kiosks to Internet connections.
Industrial
Image Recognition / Security Cameras
High-def (HD, 4K, 8K) security cameras or aggregated cameras require more uplink bandwidth. 5G’s speed and improved uplink performance support higher-definition video for improved image recognition – or to enable aggregation of multiple video streams over a single 5G router.
Augmented Reality (AR) / Virtual Reality (VR)
AR/VR goggles like Microsoft HoloLens are connecting over Wi-Fi today. They need a 5G router to connect to a private mobile network deployed in a smart factory. With Wi-Fi 6 radios, Digi EX50 5G offers better uplink QoS through UL-OFDMA, providing a better video link with less lag.
Network Slicing
Carriers use network slicing to tailor the 5G network to specific use cases, such as high-bandwidth, low-latency, massive IoT or a hybrid. They may also offer a regional or nationwide private cellular network slice to customers.
Transportation
Connected Vehicles
Transportation is evolving with assisted driving and automated guided vehicles, on public roads as well as in smart factories and smart warehouses. These vehicles will transport passengers and goods alike. Digi TX64 5G provides the reliable, high-speed and low latency link between the vehicle and its infrastructure.
Premium Wi-Fi
City infrastructure is growing rapidly and becoming smarter and more connected every day. From live-streaming of high-def multi-camera footage and real-time bus fleet occupancy reporting to great passenger Wi-Fi, the Digi TX64 5G router makes it all happen.
Sunsetting Technology
Today, 2G and 3G cellular networks are rapidly sunsetting to make room for new spectrum. 4G LTE shares spectrum with 5G, making it possible to maintain 4G deployments and begin adding 5G routers to extend the life of your infrastructure and allowing to roll out new use cases as the 5G infrastructure grows.
Frequently Asked Questions About 5G
When will 5G be fully deployed?
5G networks are rapidly rolling out and those who want to deploy can do so now. Full 5G deployment will take another decade, but in many urban areas 5G is already fully operational. The good news is that 5G and 4G LTE will co-exist for many years to come. So, whether you want to future proof your deployment with new 5G solutions now, or continue with 4G LTE, you can’t go wrong. For many applications operating well on LTE networks or that do not require 5G performance, it may be another 5-10 years before it makes sense to upgrade.
Digi operates in the commercial space, serving commercial, industrial, medical and government entities and developers. For this reason, information on this page is geared toward these customers. See your mobile phone vendor or carrier for updates on the timeline for handheld 5G devices.
Will 5G be the right solution for every application?
The right solution for any specific application depends upon the business case. Not every application is ready – or right for 5G. The key considerations include:
- Analysis of the application’s network speed and throughput requirements.
- Analysis of 5G availability in the application’s deployment area.
- Analysis of 5G costs, based on the deployment scope and scalability requirements.
When will 5G be a standard?
5G is already an official technology standard, via 3GPP Release 15, which was released in December 2018.
The "million dollar question" is really about when will 5G be everywhere, with the carrier-promised speed, latency and density. Today, enough 5G infrastructure is deployed nationwide for the majority of applications to fully benefit from 5G. The Ericsson Mobility Report predicts that by 2031, the thirds of mobile subscriptions will be 5G.
When will 2G and 3G be phased out?
Carriers are currently in the process of phasing out 2G and 3G networks, as they need to replace them with more up-to-date networks, rather than maintain everything from 2G to 5G, which is costly and labor-intensive. See our article, Upcoming 2G and 3G Global Cellular Network Sunset Dates, for a roadmap of projected shutdown dates by region and carrier.
Will 4G LTE be sunsetted as well?
For those who have made investments in 4G LTE technology or are preparing to deploy devices now, there is very good news. 4G LTE networks and devices will migrate to 5G over time, without the requirement to replace all of your equipment. As LTE stands for Long Term Evolution, this infrastructure has a long life ahead, thanks to a new technology called Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS). DSS allows 4G and 5G devices to share the same band, resulting in a faster rollout of 5G and long-term availability of 4G, as spectrum does not have to be taken away from 4G to support 5G.
Digi International works with customers who are ready to define their path to 5G to ensure they can sort through the massive amounts of information, perform a careful needs assessment, and identify the right solution. Contact us for a consultation to learn more about 5G planning and 5G technology selection.
How can I prepare for 5G?
Digi proposes that customers who are certain they want to migrate to 5G as soon as possible plan for a three-phase approach:
| Phase |
Objective |
Recommended Actions |
Customer Value |
| Phase 1: Modernize the Foundation |
Prepare the network for long-term wireless evolution |
Replace legacy equipment with modern 4G LTE or LTE-Advanced platforms.
Refresh older LTE routers with 5G-ready or LTE-Advanced solutions.
Standardize on centralized device management and security. |
Improves performance and longevity while ensuring readiness for 5G without forcing immediate change. |
| Phase 2: Adopt 5G Strategically |
Introduce 5G where it delivers measurable benefit |
Add 5G using an extender connected to an existing router, or upgrade to an integrated 5G router.
Maintain hybrid 4G/5G connectivity for resilience.
Select indoor or outdoor solutions based on environment and coverage. |
Enables faster speeds, better uplink, and lower latency while minimizing disruption and preserving flexibility. |
| Phase 3: Scale and Optimize |
Maximize performance, resilience, and operational efficiency |
Expand with outdoor 5G extenders for improved signal quality and multi-carrier redundancy.
Implement intelligent failover, centralized monitoring, and advanced security.
Optimize data usage and lifecycle management. |
Delivers high availability, improved visibility, and a scalable architecture ready for future 5G capabilities. |
What services and use cases will use 5G technology?
In general, 5G use cases can be broadly categorized into three main types of connected services:
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband: 5G will not only make our smartphones better, but it will also support new immersive experiences, such as VR and AR, with faster, more uniform data rates, lower latency, and cost-per-bit. This will be especially important for field service technicians, for example, who have to repair sophisticated systems and machines.
- Mission-Critical Applications: 5G will enable new services that can transform industries with ultra-reliable/available, low latency links — such as remote control of critical infrastructure, vehicles, and medical procedures.
- Massive Internet of Things: 5G will seamlessly connect a massive number of embedded sensors in virtually everything through the ability to scale down in data rates, power and mobility to provide extremely lean/low-cost solutions.
A defining capability of 5G is also the design for forward compatibility — the ability to flexibly support future services that are unknown today.
How fast is 5G?
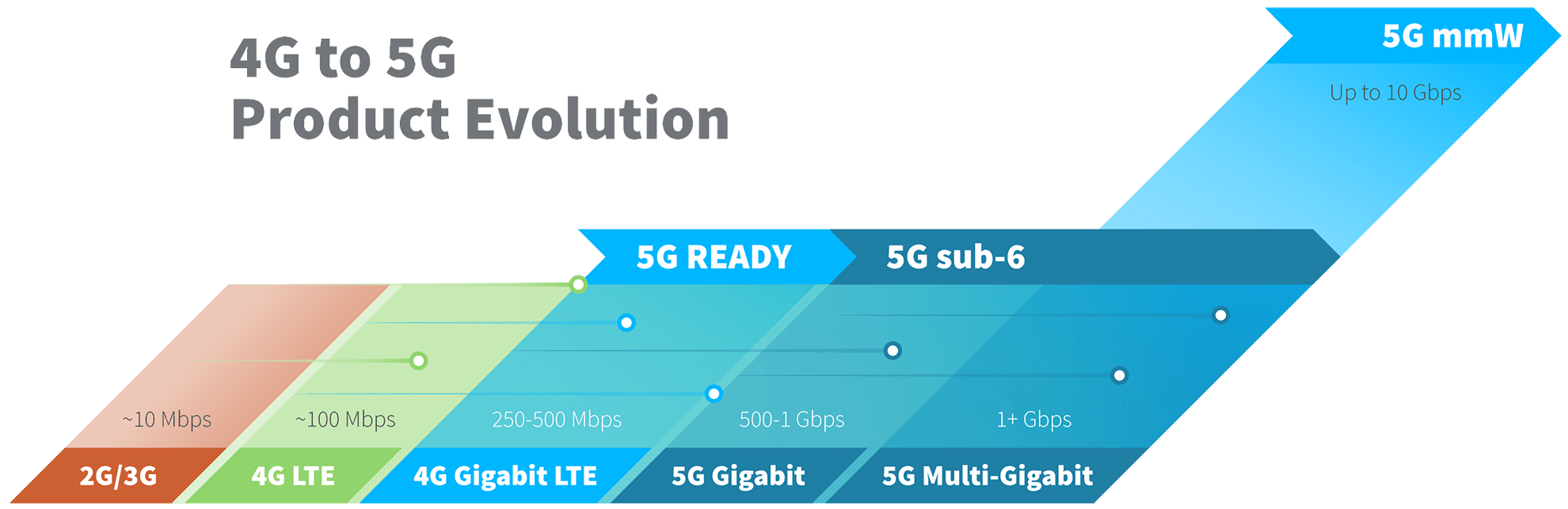
5G was designed to support theoretical peak data rates of up to 20 Gbps, but real-world performance varies based on spectrum type, network configuration, device capabilities, and carrier deployment.
Today, most 5G deployments use sub-6 GHz spectrum, where typical speeds often range from modest improvements over advanced 4G LTE to several hundred Mbps. In some locations, sub-6 GHz 5G performance may be similar to LTE-Advanced, particularly where spectrum bandwidth is limited.
Millimeter wave (mmWave) 5G can deliver multi-gigabit speeds — often exceeding 1–2 Gbps — but availability is limited to dense urban areas and specific use cases due to its shorter range and line-of-sight requirements.
5G is about more than peak speed alone. Its primary advantages include increased network capacity through access to new spectrum, improved uplink performance, and lower latency—particularly as carriers transition to 5G Standalone (SA) architectures. These capabilities enable more consistent performance, better support for high-density deployments, and improved responsiveness for latency-sensitive applications.
In practice, 5G and advanced LTE technologies operate together, with LTE-Advanced continuing to provide broad coverage and reliability while 5G adds capacity and performance where available.
This hybrid approach ensures a consistent, resilient user experience as networks continue to evolve.
How much does 5G cost?
5G does not have a single, universal price. Today, 5G service is typically priced similarly to 4G LTE, with costs determined by factors such as data usage, service level, coverage, and carrier plan structure. In many cases, 5G is included in existing data plans rather than offered as a separate premium service.
One of the core design goals of 5G is to improve network efficiency and reduce the cost per bit for mobile operators by using wider channels and additional spectrum, including mid-band and millimeter wave frequencies. While this increased efficiency helps carriers manage growing data demand, it does not necessarily translate to unlimited data or lower costs for every use case.
For enterprises and IoT deployments, overall cost is influenced by device capabilities, data consumption patterns, management requirements, and service reliability—not just peak throughput. As a result, many organizations deploy 5G alongside 4G LTE, using each technology where it delivers the best balance of performance, coverage, and cost.
Rather than focusing on a fixed price for 5G, organizations should evaluate total cost of ownership, including hardware, connectivity, management, and lifecycle considerations, when determining how and where 5G fits into their network strategy.