Embedded systems are at the heart of many different products, machines and intelligent operations, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence applications. As embedded systems applications appear in every industry and sector today, embedded devices and software play a crucial role in the functioning of cars, home appliances, medical devices, interactive kiosks, and other equipment we use in our daily lives. In this article, we have provided embedded system examples with explanations to help you learn how this technology is impacting every facet of modern life.
While real life
embedded systems have become a significant part of our lives, they are engineered to operate with minimal human intervention. Characteristics like compact size, simple design, and low cost make them a useful technology in industries like aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and even smart cities. Thus, they are one of the driving forces behind today’s digital, connected, and automated world. Here you will find the types and characteristics of embedded systems along with some real-life examples of devices running embedded software.
4 Types of Embedded Devices

Common embedded systems can be broken into four types based on performance as well as functional requirements:
- Real-time
- Stand-alone
- Networked
- Mobile
Real-Time
Real-time embedded systems are designed and installed to carry out specific tasks within a pre-defined time limit. They are further divided into two different types:
- Soft Real-Time Embedded Systems: For these systems, the completion of the task is of paramount importance, while the deadline is not a priority.
- Hard Real-Time Embedded Systems: These systems prioritize deadlines, so they shouldn’t be missed in any case.
Some of the real-time embedded systems examples are:
- Sound System of a computer (Soft real-time system)
- Aircraft control system (Hard real-time system)
Stand-alone
These are self-sufficient systems that do not rely on a host system like a processor or a computer to perform tasks. Here are some standalone embedded technology examples:
- Microwave ovens
- Washing machines
- Video game consoles
Networked
These systems are connected to a wired or wireless network to perform assigned tasks and provide output to the connected devices. They are comprised of components like controllers and sensors. Here are some network embedded software examples:
- ATMs
- Home security systems
- Card swipe machines
Mobile
These systems are smaller in size and easy to use. Though they come with limited memory, people still prefer them due to their portability and handiness. Here are a few mobile embedded control systems examples:
- Digital cameras
- Mobile phones
- Smart watch
- Fitness tracker
Characteristics of Embedded Computer Systems
The main characteristics of typical embedded systems include:
- Small Form Factor (SFF): These are PCB designs packed with robust processing power in smaller rugged enclosures, which maximizes space efficiency.
- Power efficient components: These are processors with lower thermal design power that minimize cooling and eradicate the need for fans as well as moving components.
- Single-functioned: These systems are designed to perform a specific operation during their lifetime.
- Lower cost: Since they don’t feature expansion slots for peripherals, embedded systems are generally lower cost than full-featured computers and have fewer component complexities.
If you are not familiar with embedded systems terminology or concepts and want to know more, we have many resources available. See the Related Content at the bottom of this page, as well as our Resources, Solutions pages and Videos.
10 Embedded Systems Examples
There are many things with embedded systems incorporated in the Internet of Things (IoT), as well as in machine to machine (M2M) devices. Exceptionally versatile and adaptable, embedded systems can be found in all smart devices today. It is difficult to find a single portion of modern life that doesn’t involve this technology. Here are some of the real-life examples of embedded system applications.
- Central heating systems
- GPS systems
- Fitness trackers
- Medical devices
- Automotive systems
- Transit and fare collection
- ATMs
- Factory robots
- Electric vehicle charging stations
- Interactive kiosks
1. Central Heating Systems

Central heating systems convert the chemical energy into thermal energy in a furnace room and transfer that energy into heat, which is then delivered to numerous spaces within a building. It is important for these systems to have thermostat controls to adjust the temperature, which is achieved by an embedded system.
If a central heating system isn’t provided with temperature controls, it can lead to overheating one room while leaving another room cold. The right thermostat controls will allow you to adjust the temperature to a comfortable level and save energy extensively.
Embedded system examples in central heating can be found in a range of structures that require temperature control, both for comfort and for management of temperature-sensitive goods.
Examples include:
- Office buildings
- Factories
- Grocery stores
- Homes
- Schools
- Hospitals
2. GPS Systems

The GPS is a navigation system that uses satellites and receivers to synchronize data related to location, time, and velocity. The receiver or device that receives the data has an integrated embedded system to facilitate the application of a global positioning system. The embedded GPS devices allow people to find their current locations and destinations easily. Thus, they are gaining rapid momentum and becoming the most widely used navigation tools for automobiles.
Nowadays, GPS systems are generally used in:
- Cars
- Mobile devices
- Palmtop
3. Fitness Trackers

Fitness trackers are wearable devices that can monitor your health and track activities like sleeping, running, and walking. These devices use embedded systems to garner data related to your heart rate, body temperature, and the number of footsteps, which is further sent to servers via WAN like LTE or GPRS.
Fitness trackers are generally used for:
- Monitoring personal activity
- Medical monitoring
- Sports training
4. Medical Devices
Medical devices in healthcare facilities have been incorporating embedded systems for quite some time. A new class of medical devices use embedded systems to help treat patients who need frequent monitoring and constant attention at home. These systems are embedded with sensors to gather data related to patients’ health like heart rate, pulse rate, or readings from implants, which are sent to a cloud where a doctor can review patient data on their device wirelessly. Medical devices have been widely used for diagnosing and treating patients efficiently, and some of their examples are:
- Pacemaker
- Defibrillator
- Ultrasound scanners
Get Our Solution Brief
Learn about security and reliability in connected medical devices
Download PDF
5. Automotive Systems
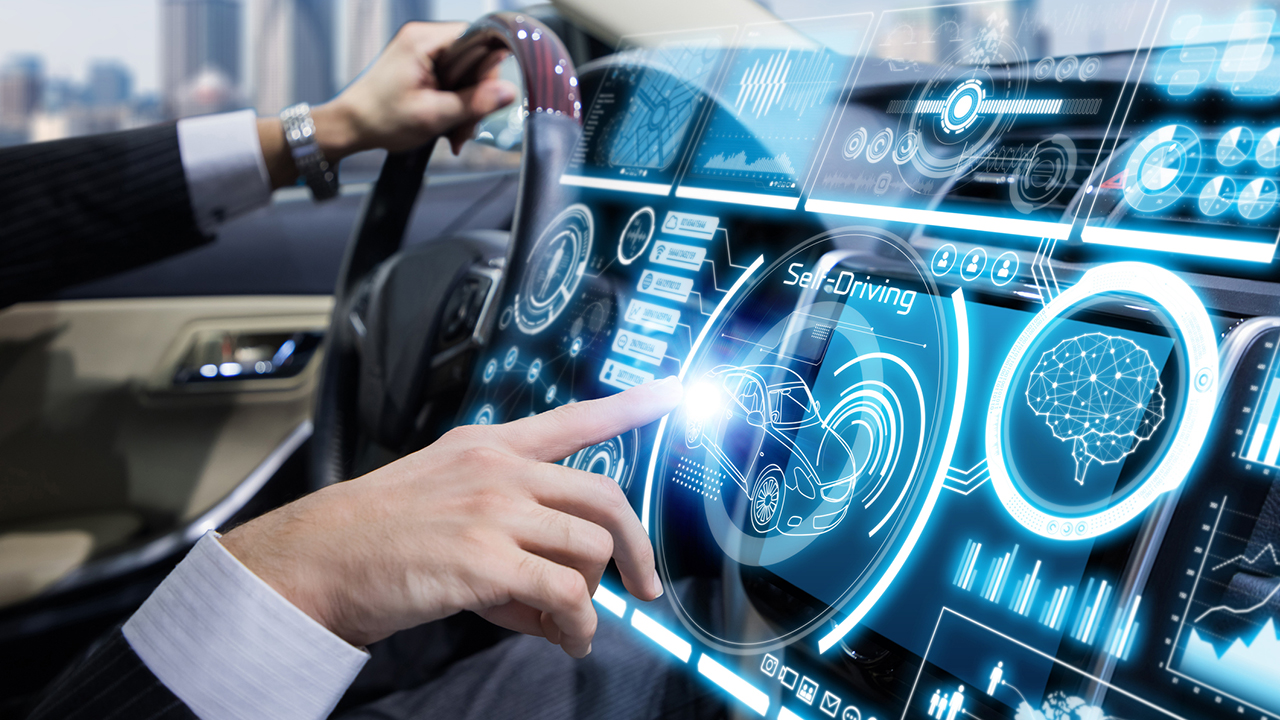

Automotive embedded systems are designed and installed to enhance the safety of automobiles. Thanks to the safety systems in vehicles, the traffic fatality rate has plummeted in recent years. Automobile industries are going the extra mile to reinforce automobiles with advanced technology systems and sensors, which is not possible without embedded systems.
Some key examples of an active safety system include adaptive speed control, car breakdown warning, pedestrian recognition, merging assistance, airbags, and more. These are a few features anticipated to mitigate the risk of accidents and foster the demand for embedded systems across the globe.
Some more examples of automotive embedded systems include:
- Car navigation system
- Anti-lock braking system
- Vehicle entertainment system
6. Transit and Fare Collection
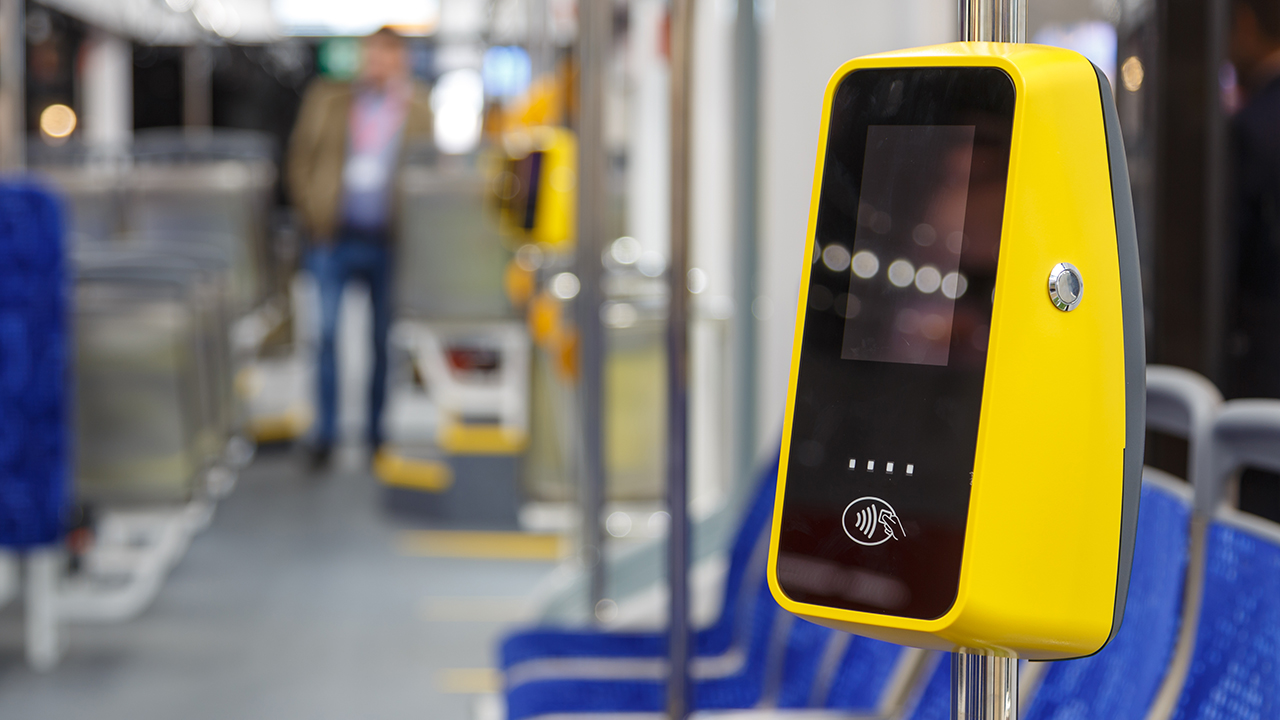

Automated Fare Collection (AFC) is a ticketing system that allows passengers to pay the fare through ticket vending machines or online services. These systems were originated with coins and tokens but have been replaced with magnetic stripe cards or smart cards. An AFC is a basic station device comprising a ticket vending machine, automatic gate machine, and ticket checking machine. These components are embedded systems that ensure faster transactions, seamless operations, and more efficient payment collection.
While city transit bus and commuter rails still use paper tickets and passes, urban transit systems have adopted AFC with smart cards, which are inexpensive technologies and offer additional security along with data collection options.
Automated fare collection systems are generally found at:
- Metro stations
- Bus stations
- Railway stations
If you are looking for embedded processor examples in the transportation sector, see some of our customer stories, sharing how Digi embedded System-on-Modules are designed into transit and vehicle applications:
7. ATMs
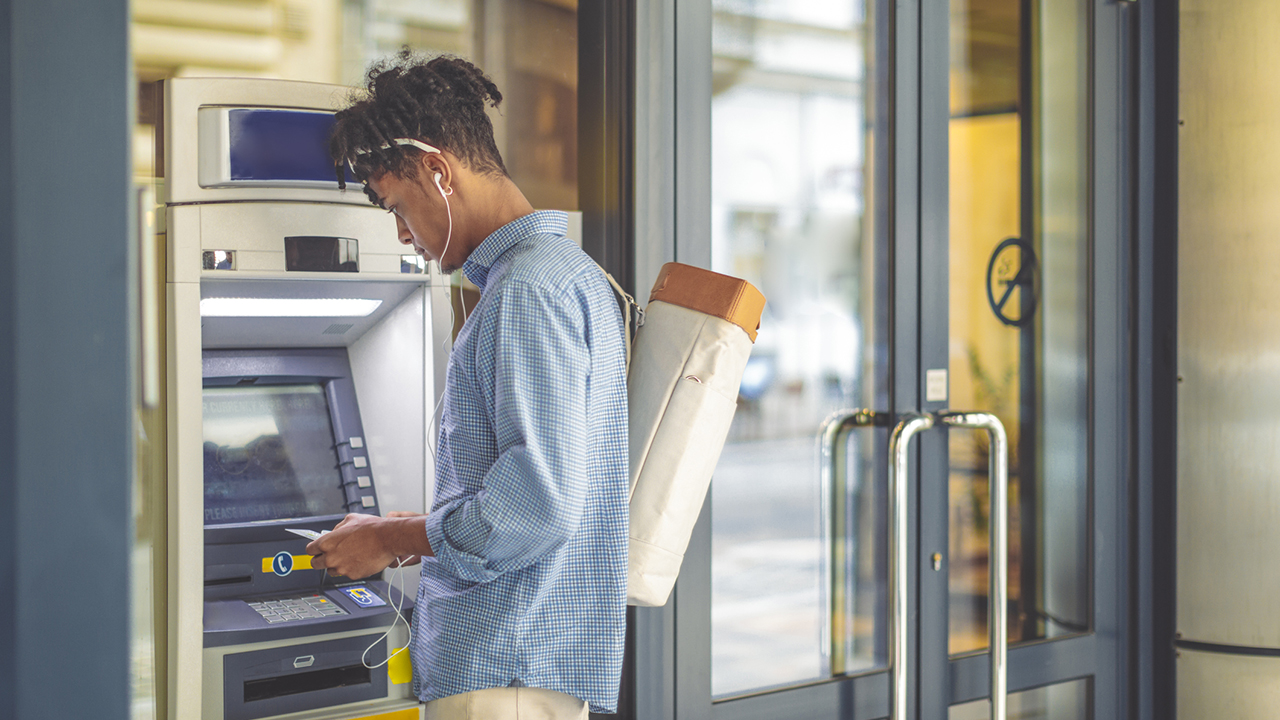

An automated teller machine (ATM) is a computerized machine used in banking that communicates with a host bank computer over a network. The bank computer verifies all the data entered by the users and stores all transactions, while the embedded system in the ATM displays the transaction data and processes inputs from the ATM keyboard.
An ATM is mostly used to:
- Withdraw cash
- Check account balance and transactions details
- Deposit money into another account
8. Factory Robots
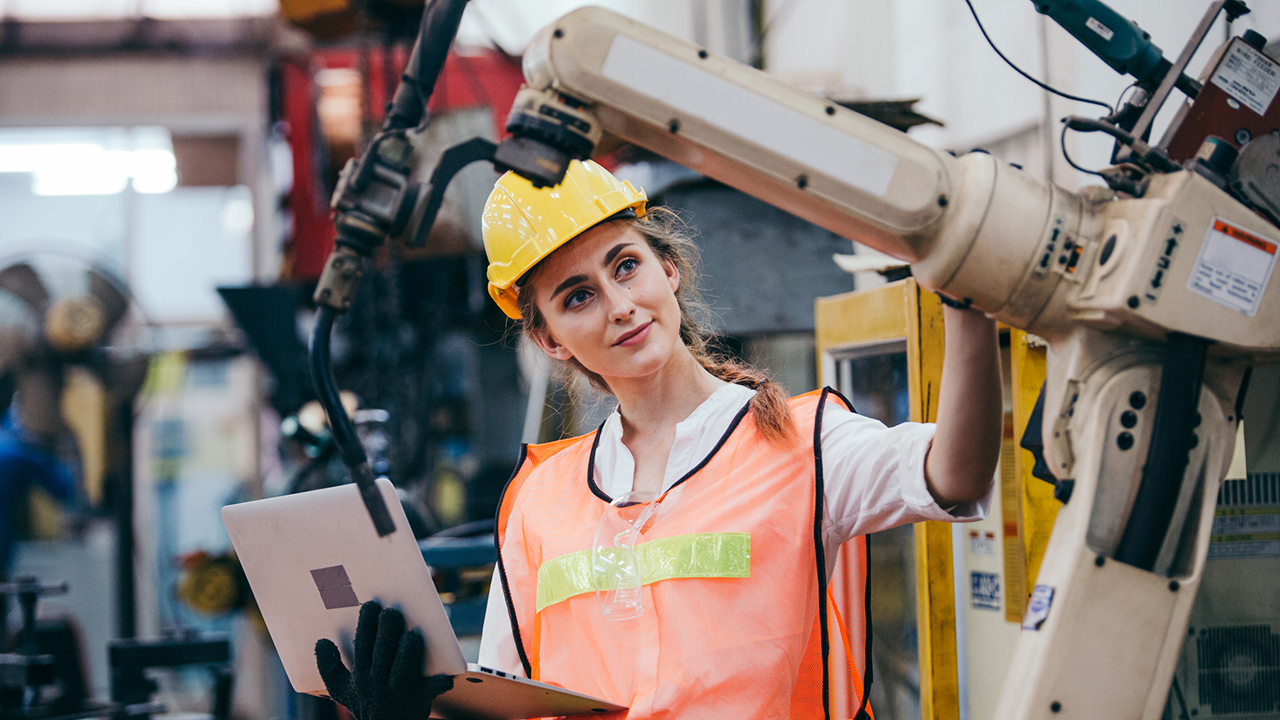

Factory robots are designed to perform high-precision tasks under dangerous work conditions. They have an integrated embedded system to connect different subsystems. In a typical mechanical job, robots employ actuators, sensors, and software to perceive the environment and derive intended output safely.
Without an embedded system, robots would have to rely on external control or computing systems. This, in turn, can elevate the safety risks due to delay or failure in the connection link between the factory robot and its external computing system. Today, as Industry 4.0 comes to fruition, these systems are integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning to make equipment smarter, safer and more effective — for example, enabling machines to identify defects that the human eye wouldn't see, and remove these from production.
Factory robots have a range of applications:
- Assembly line
- Quality monitoring
- Welding
- Painting
- Palletizing
9. Electric Vehicle Charging Stations
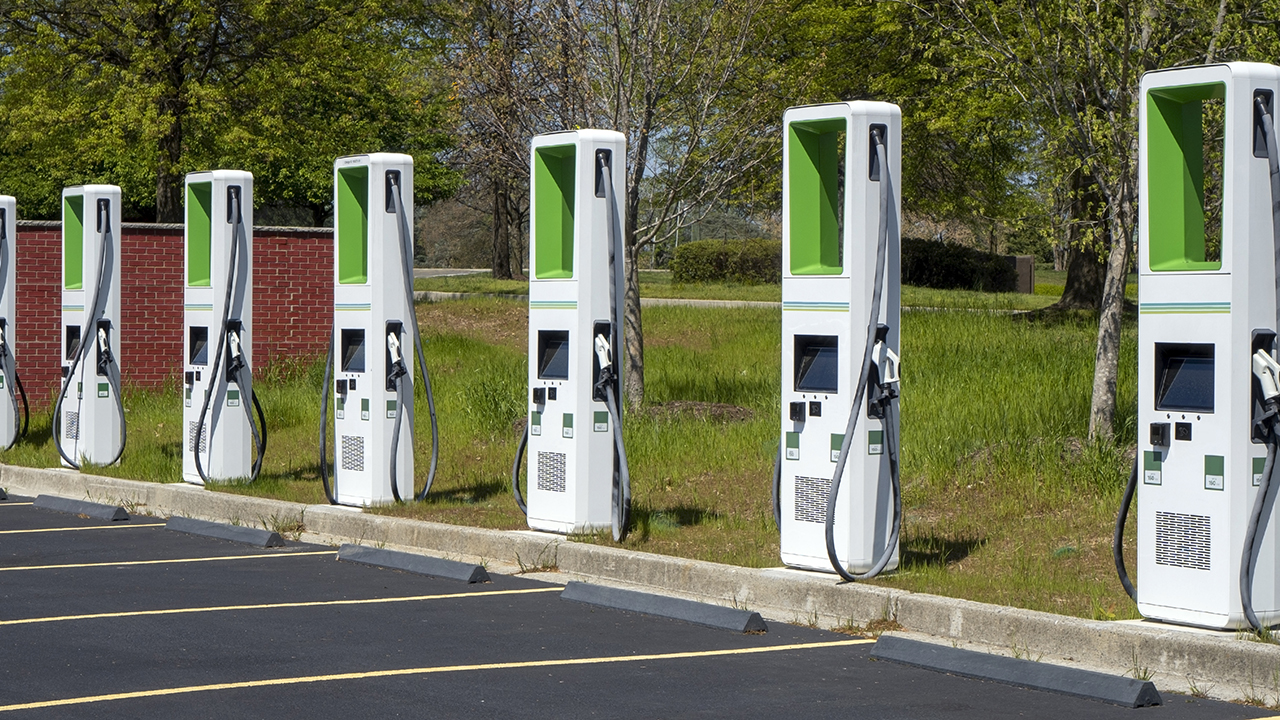

Electric vehicle charging stations are equipped with charging points or units that supply electric power to charge connected vehicles. An embedded system resides in the charging station to provide processing for graphics displays, report any issues with the device and alert technicians when maintenance is required. This embedded solution provides an easy and cost-effective approach to monitoring and maintaining the charging infrastructure. A number of Digi customers, such as AddÉnergie, are developing solutions to serve this growing market.
Some of the common uses of electric vehicle charging stations include:
- Charging vehicles
- Swapping batteries
- Parking vehicles
10. Interactive Kiosks
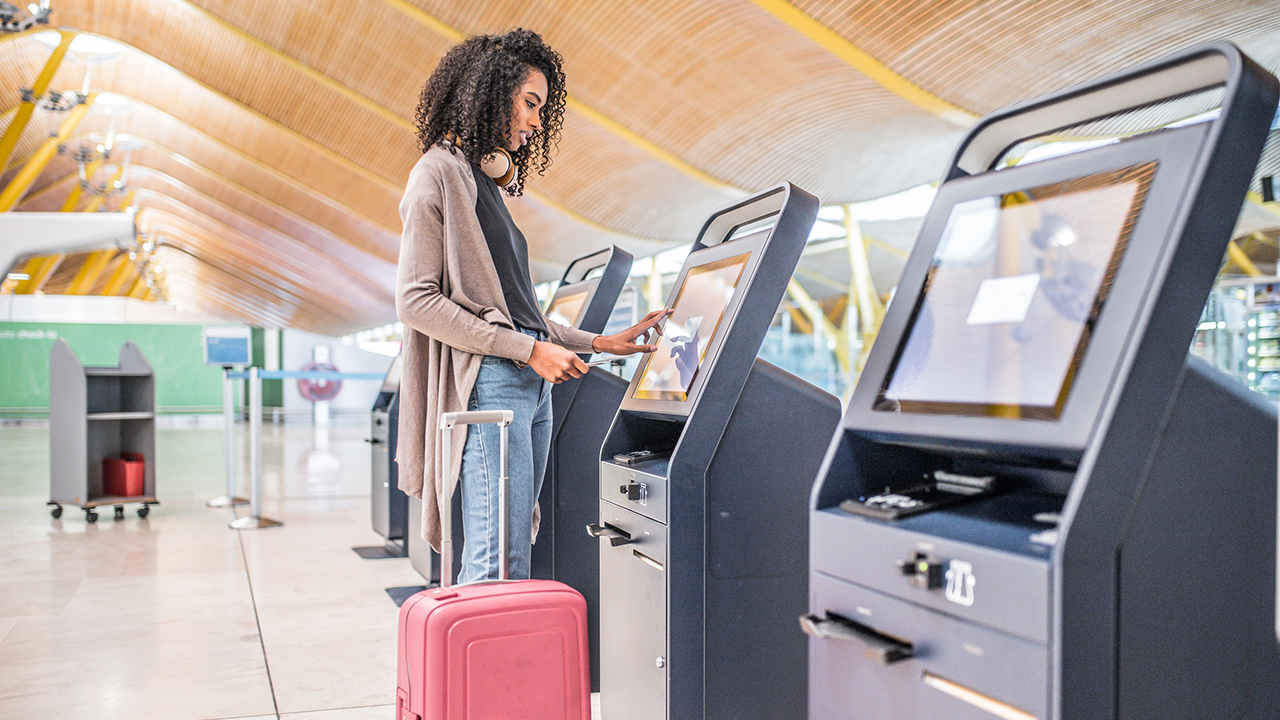

Self-service kiosks are designed to offer services and information to end-users in environments where human employee presence isn’t possible or cost-effective. For instance, these machines and terminals allow a passenger in an empty airport to buy a meal at 4 am without interacting with human workers. Interactive kiosks come in all shapes and sizes, from simple coffee dispensing systems to complex vending machines and fuel stations with high-definition graphics. For this reason, it is important for embedded developers to work with a scalable product line like Digi ConnectCore® 8X/8M system-on-modules (SOMs), which support development of product lines with scaling levels of functionality.
An embedded system provides the processing for connected, self-service kiosk machines, offering an interactive consumer experience. These systems can be developed to function in remote and outdoor environments and deliver information and services even in extreme weather conditions. They can also eliminate downtime for real-time applications and have expandable I/O options designed for workload consolidation.
Apart from airports, interactive kiosk machines are mostly found in:
- Retail sites and convenience stores
- Hospitals
- Movie theaters
- Government buildings
The Importance of Embedded Systems

People often question the importance of embedded systems in daily life. These small computers are integrated into various systems for performing specific image and data processing tasks, and thus significantly impact the way we commute, spend our leisure time, run business, and perform various other daily activities.
Still wondering where can you find embedded systems? Whether you work in a restaurant, office, health practice, factory or other environment, your workplace is full of systems that are built with embedded devices, like elevators, printers, routers and point of sale systems. In brief, they can be found everywhere in our society — from vehicles and EV charging stations to vending machines, lottery ticket systems and digital signage to sophisticated medical equipment.
Here are some of the reasons why embedded systems are becoming prevalent across the globe:
- They are small, fast, and powerful computers used in many devices and equipment we use daily.
- They guarantee the performance of real-time applications.
- They are responsible for the completion of a task within a specified time limit, such as rapid graphics processing and artificial intelligence processing.
Additionally, embedded modules are becoming more sophisticated and powerful all the time, and are increasing in graphics performance and edge compute capabilities, giving embedded developers the tools to bring high-performance market-driven products to market.
Find Your Embedded Systems Solutions with Digi
The significance of embedded systems is so much that the world without them would look considerably different than it does today. Thanks to the continuous tech advancements, they will become more crucial for every device in the foreseeable future. Understanding why we use embedded systems and a plethora of examples where they are installed will make you better equipped to perceive the tech world around you and leverage the benefits of this exciting technology.
At Digi, we’ve taken embedded systems and development tools to the next level. Our embedded systems are complete solutions for wireless application development, with developer tools and built-in security. Learn more about our embedded systems solutions and contact us to start a conversation.
Next Steps