IoT in logistics is transforming traditional supply chains into smart, connected ecosystems that address modern operational challenges. As organizations face increasing demands and cost pressures, Internet of Things and logistics solutions deliver measurable outcomes through real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and automated operations.
This exploration showcases how the IoT drives innovation and automation across supply chain management, reducing costs while enhancing safety compliance.
Discover cutting-edge connectivity solutions by downloading our guide on leveraging the power of remote management in IoT.
The Future of the Internet of Things in Logistics
The Internet of Things in logistics landscape is experiencing unprecedented growth and transformation. The IoT-powered logistics market was valued at USD 42.3 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 146.1 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 13.2% during the forecast period 2024-2033. This explosive growth reflects the industry's recognition of IoT and logistics integration as essential for competitive advantage. The Internet of Things supply chain revolution is driven by increasing digitalization demands, e-commerce expansion, and the need for enhanced supply chain visibility following global disruptions.

Key statistics illustrating the impact of IoT in logistics include:
- Market growth: Logistics IoT spending is on track to surge from US$50.26 million to US$189.62 million by 2034 (CAGR 14.2%)
- Fleet segment dominance: The fleet segment dominated the market with the most significant revenue of US$11.8 billion, where IoT improves driver safety, eliminates driver fraud, prolongs vehicle life, and aids logistics firms in more effectively managing fuel and maintenance expenses
- Supply chain IoT expansion: Supply Chain IoT Market size was valued at US$21.36 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach US$55.58 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 12.70% from 2024-2031
- Transportation technology growth: The global IoT in transportation market is poised to grow at a CAGR of 21.69% from 2024 to 2034
AI and Machine Learning in Logistics
AI and machine learning amplify IoT in logistics by transforming sensor data into actionable insights. AI-powered analytics optimize forecasting by 50%, while predictive maintenance reduces downtime. Machine learning enhances inventory planning via pattern recognition and seasonal modeling, enabling data-driven decisions that improve delivery speed and efficiency.
Blockchain for Transparency and Security
Blockchain strengthens Internet of Things in supply chain management by creating immutable transaction records and enhancing traceability. This technology provides validated, immutable records for all parties, reducing errors and increasing transparency. Blockchain enables real-time shipment tracking and automated contract execution, addressing trust challenges in logistics operations.
5G and Enhanced Connectivity
5G networks revolutionize IoT logistics by providing ultra-low latency communication and massive device connectivity. This enhanced connectivity enables you to implement real-time fleet monitoring, autonomous vehicle operations, and instantaneous data transmission that powers next-generation logistics automation.

The benefits of IoT in supply chain operations extend across every aspect of logistics management, from cost reduction to enhanced customer satisfaction. Modern IoT in logistics implementations deliver measurable improvements in operational efficiency, safety compliance, and environmental sustainability. Organizations leveraging Internet of Things supply chain solutions report significant gains in visibility, asset utilization, and predictive maintenance capabilities that translate directly to competitive advantages.
- Lower operational costs
- Efficiency
- Real-time visibility
- Enhanced safety and compliance
- Minimized asset loss and theft
- Improved environmental impact
Lower Operational Costs
IoT in logistics reduces operational expenses through automated monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimized resource allocation. Smart sensors eliminate manual inspection costs, while predictive analytics prevent costly equipment failures. Fuel optimization algorithms reduce transportation costs by 10-15% through route optimization. Advanced LTE connectivity solutions enable cost-effective remote monitoring across distributed logistics networks.
Efficiency
IoT logistics solutions streamline operations through automation, real-time coordination, and process optimization that improve throughput while reducing delays. Automated inventory systems increase picking accuracy by 99.5%, while smart routing algorithms optimize delivery schedules. Centralized device management platforms enable remote configuration and monitoring of thousands of connected devices, reducing manual intervention requirements.
Real-Time Visibility
Internet of Things and logistics integration provides unprecedented visibility into supply chain operations through continuous monitoring and instant status updates. Real-time tracking systems reduce shipment delays by 25% through proactive issue identification. Reliable connectivity solutions ensure consistent data transmission even in challenging environments, enabling complete transparency across global supply chains.
Enhanced Safety and Compliance
IoT in logistics improves safety through continuous monitoring of driver behavior, vehicle conditions, and environmental factors while ensuring regulatory compliance. Smart sensors detect safety violations instantly, while automated reporting systems maintain compliance documentation. End-to-end security frameworks protect sensitive logistics data, meeting stringent industry regulations while maintaining operational safety standards.
Minimized Asset Loss and Theft
Internet of Things in logistics reduces asset loss through real-time tracking, geofencing alerts, and tamper detection systems. GPS-enabled devices provide precise location data, while motion sensors detect unauthorized access attempts. Smart locks prevent theft, while automated alerts notify operators of suspicious activities. These measures reduce asset loss by 40%.
Improved Environmental Impact
IoT and logistics support sustainability goals through optimized routing, reduced fuel consumption, and efficient resource utilization. Smart sensors monitor vehicle emissions and energy usage, enabling companies to reduce their carbon footprint by 20-30%. Edge computing solutions process data locally, reducing cloud transmission requirements while supporting environmental compliance monitoring.

The Internet of Things in supply chain management encompasses diverse applications that transform traditional logistics operations into intelligent, connected ecosystems. From warehouse automation to cold chain monitoring, IoT in logistics applications address critical operational challenges while improving service quality and cost efficiency. These implementations demonstrate the versatility and impact of IoT in SCM across different logistics segments, from last-mile delivery to global freight management. Modern Internet of Things supply chain applications integrate seamlessly with existing systems while providing scalable solutions for future growth.
- Real-time shipment monitoring
- Inventory management
- Cold chain monitoring
- Vehicle tracking and driver monitoring
- Fleet management and predictive maintenance
- Warehouse automation and robotics
IoT solutions enable continuous shipment tracking through GPS sensors, RFID tags, and cellular connectivity that provide precise location data and delivery status updates. Smart sensors monitor package conditions including temperature, humidity, and shock levels throughout transit. Real-time alerts notify stakeholders of delays, route deviations, or handling issues, enabling proactive intervention. Advanced tracking systems reduce lost shipments by 95% while improving customer satisfaction through accurate delivery predictions and transparent communication.
Inventory Management
The IoT revolutionizes inventory management through automated stock monitoring, predictive replenishment, and real-time visibility across multiple locations. RFID and sensor technologies provide accurate inventory counts, reducing stock-outs by 50% while minimizing excess inventory. Smart shelving systems automatically track product movement and trigger reorder alerts. Predictive analytics optimize inventory levels based on demand patterns, seasonal trends, and supply chain dynamics, ensuring optimal stock availability while reducing carrying costs.

Cold Chain Monitoring
IoT logistics solutions ensure temperature-sensitive products maintain quality through continuous environmental monitoring and automated alerts. Smart sensors track temperature, humidity, and other critical parameters throughout the cold chain journey. Real-time data transmission enables immediate corrective action when conditions deviate from acceptable ranges. These systems reduce product spoilage by 30-40% while ensuring compliance with food safety and pharmaceutical regulations. Automated documentation provides complete audit trails for regulatory compliance and quality assurance.
Vehicle Tracking and Driver Monitoring
Internet of Things in logistics provides comprehensive vehicle and driver monitoring through GPS tracking, telematics, and behavioral analytics. Smart devices monitor vehicle performance, fuel consumption, and maintenance needs while tracking driver behavior including speed, acceleration, and rest periods. Real-time alerts improve safety by detecting fatigue, aggressive driving, or vehicle malfunctions. These systems reduce accidents by 25% while improving fuel efficiency through optimized routing and driver coaching programs.
Fleet Management and Predictive Maintenance
IoT in logistics transforms fleet operations through predictive maintenance, performance optimization, and automated scheduling systems. Sensors monitor engine parameters, tire pressure, brake conditions, and other critical components to predict maintenance needs before failures occur. Predictive analytics reduce unplanned downtime by 70% while extending vehicle lifespan. Real-time performance data enables route optimization, load balancing, and fuel efficiency improvements that reduce operating costs while improving service reliability.
Warehouse Automation and Robotics
Internet of Things supply chain integration enables intelligent warehouse operations through robotics, automated systems, and real-time coordination platforms. Connected devices optimize picking routes, coordinate inventory movement, and manage automated storage systems. IoT and logistics platforms orchestrate complex warehouse operations while providing real-time visibility into productivity metrics and system performance.
- Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs): Navigate warehouses independently
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): Transport goods across warehouses
- Robotic picking systems: AI-driven robotic arms improve picking speed and accuracy
- IoT-enabled conveyor systems: Optimize package sorting and handling

Internet of Things in logistics encompasses diverse technologies that enable comprehensive monitoring, communication, and automation across supply chain operations. These technologies work synergistically to create intelligent logistics networks that adapt to changing conditions, optimize performance, and provide unprecedented visibility. From edge computing to advanced connectivity solutions, IoT logistics technologies form the foundation for next-generation supply chain management systems that deliver measurable business value.
Remote Sensors
Remote sensors form the foundation of IoT in logistics by collecting real-time data on location, condition, and environmental parameters throughout the supply chain. These devices monitor temperature, humidity, vibration, light exposure, and other critical factors that affect product quality and safety. Advanced sensors provide precise measurements with extended battery life and robust connectivity options. They solve visibility challenges by providing continuous monitoring without manual intervention, enabling proactive decision-making and quality assurance.
Connectivity Solutions
Connectivity technologies enable seamless communication between devices, systems, and stakeholders in Internet of Things and logistics applications. Cellular, Wi-Fi, satellite, and low-power wide-area networks provide reliable data transmission across diverse operating environments. Multi-network capabilities ensure continuous connectivity even in remote locations or challenging conditions. These solutions solve communication gaps by providing redundant connectivity options, enabling real-time coordination and remote monitoring across global logistics networks.
Data Analytics and Edge Computing
Data analytics platforms transform raw sensor data into actionable insights for IoT logistics optimization. Machine learning algorithms identify patterns, predict trends, and recommend actions based on historical and real-time data. Advanced analytics enable demand forecasting, route optimization, and predictive maintenance that improve efficiency and reduce costs. Edge computing processes data locally, reducing latency and bandwidth requirements while enabling real-time decision-making for time-critical logistics operations.
Edge Computing and Cloud Integration
Edge computing brings processing power closer to Internet of Things in logistics devices, enabling real-time data analysis and rapid response capabilities. Cloud integration provides scalable storage, advanced analytics, and centralized management for distributed logistics networks. Hybrid architectures optimize performance by processing time-sensitive data at the edge while leveraging cloud resources for complex analytics and long-term storage. This combination delivers the responsiveness needed for modern logistics operations while maintaining comprehensive data management capabilities.
While IoT in logistics offers transformative benefits, implementation challenges require careful consideration and strategic solutions. Organizations must address technical, operational, and security challenges to realize the full potential of Internet of Things supply chain initiatives. Understanding these challenges enables logistics professionals to develop comprehensive implementation strategies that minimize risks while maximizing return on investment.
Interoperability
Interoperability challenges arise when diverse IoT logistics devices, protocols, and systems fail to communicate effectively, creating data silos and operational inefficiencies. Legacy systems may not support modern communication protocols, while devices from different manufacturers often use incompatible data formats. This fragmentation reduces visibility and limits the ability to coordinate operations across integrated supply chains. Centralized device management platforms simplify multi-device network operations by providing unified interfaces, standardized protocols, and automated configuration management that ensures seamless integration across diverse IoT ecosystems.
Scalability
Scalability challenges emerge as Internet of Things and logistics deployments grow from pilot projects to enterprise-wide implementations spanning thousands of devices and multiple locations. Managing device provisioning, configuration updates, and performance monitoring becomes increasingly complex at scale. Network capacity, data processing requirements, and management overhead can overwhelm traditional IT infrastructures. Cloud-based platforms ensure seamless device scaling and integration by providing automated provisioning, centralized management, and elastic resources that adapt to growing deployment requirements.
Data Security and Compliance
Data security and compliance challenges intensify as IoT in logistics systems handle sensitive information including location data, customer details, and proprietary business intelligence. Connected devices create multiple attack vectors, while data transmission across public networks introduces additional risks. Regulatory requirements for data protection and industry-specific compliance standards add complexity to security implementations. Comprehensive security frameworks offer end-to-end encryption, device authentication, and secure communication protocols that protect sensitive logistics data while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Latency and Remote Connectivity
Latency and connectivity challenges affect device performance in remote locations, underground facilities, and areas with limited network infrastructure. High latency can delay critical alerts and decisions, while intermittent connectivity creates data gaps that impact operational visibility. Traditional cellular networks may not provide adequate coverage or reliability for mission-critical logistics applications. Advanced connectivity solutions and private network options mitigate connectivity challenges by providing reliable, low-latency communication even in challenging environments through redundant network paths and optimized protocols.
Comprehensive IoT in logistics solutions address the complex challenges of modern supply chain management through integrated platforms that combine connectivity, security, and management capabilities. These solutions enable organizations to deploy, monitor, and optimize large-scale IoT implementations while ensuring security, reliability, and scalability. Advanced platforms provide the foundation for Internet of Things supply chain transformation by delivering end-to-end solutions that address real-world logistics challenges.
Digi Industrial and Transportation Cellular Routers
The Digi portfolio of cellular router solutions includes 5G and 4G LTE solutions that support the full range of connectivity requirements for supply chain use cases. These complete solutions, with integrated security and remote management, provide robust connectivity solutions for IoT logistics applications, including automation and fleet connectivity. These solutions support multiple cellular carriers, Ethernet connections, and Wi-Fi capabilities while providing enterprise-grade security. Industrial-rated enclosures ensure reliable operation in extreme temperatures, vibration, and electromagnetic interference. Advanced routing capabilities, VPN support, and dual-carrier failover options ensure continuous connectivity for critical logistics operations that depend on reliable network infrastructure.
Digi 360 IoT Solution
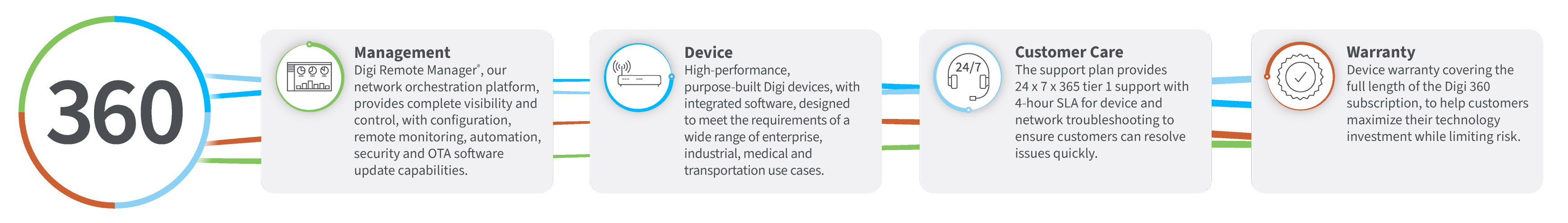 The Digi 360 IoT solution provides comprehensive end-to-end support for Internet of Things supply chain implementations, from initial design through deployment and management. This approach combines hardware, software, and services to accelerate IoT adoption while reducing risks. Professional services include system design, integration support, and training to ensure successful deployments. Ongoing services provide monitoring, maintenance, and optimization to maximize IoT investment returns while ensuring operational success.
The Digi 360 IoT solution provides comprehensive end-to-end support for Internet of Things supply chain implementations, from initial design through deployment and management. This approach combines hardware, software, and services to accelerate IoT adoption while reducing risks. Professional services include system design, integration support, and training to ensure successful deployments. Ongoing services provide monitoring, maintenance, and optimization to maximize IoT investment returns while ensuring operational success.
Digi Remote Manager
Digi Remote Manager® provides centralized management for distributed IoT logistics deployments, enabling remote configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting of connected devices across global supply chains. The platform supports diverse device types and protocols while unifying management interfaces. Automated alerts, performance monitoring, and bulk configuration reduce operational overhead while ensuring optimal performance. This comprehensive management solution enables you to scale your IoT deployments efficiently while maintaining operational excellence.
Digi CORE LTE and Private Networks
Digi CORE® LTE solutions provide high-speed connectivity for Internet of Things and logistics applications in environments where traditional networks may be inadequate. Private network capabilities ensure dedicated bandwidth, enhanced security, and predictable performance. Advanced cellular modems support multiple carriers, providing redundant connectivity options even during network disruptions. These solutions enable IoT deployments in remote locations, underground facilities, and areas with limited infrastructure.
Digi TrustFence Security Framework
The Digi TrustFence® security framework provides comprehensive protection for IoT in logistics deployments through multi-layered security that addresses device, network, and data-security requirements. The framework includes secure boot, encrypted communications, authentication protocols, and intrusion detection. Regular security updates and vulnerability management ensure ongoing protection against emerging threats. This comprehensive security approach enables organizations to deploy IoT solutions with confidence while meeting stringent industry compliance requirements.
Digi XBee Ecosystem for Wireless Communication
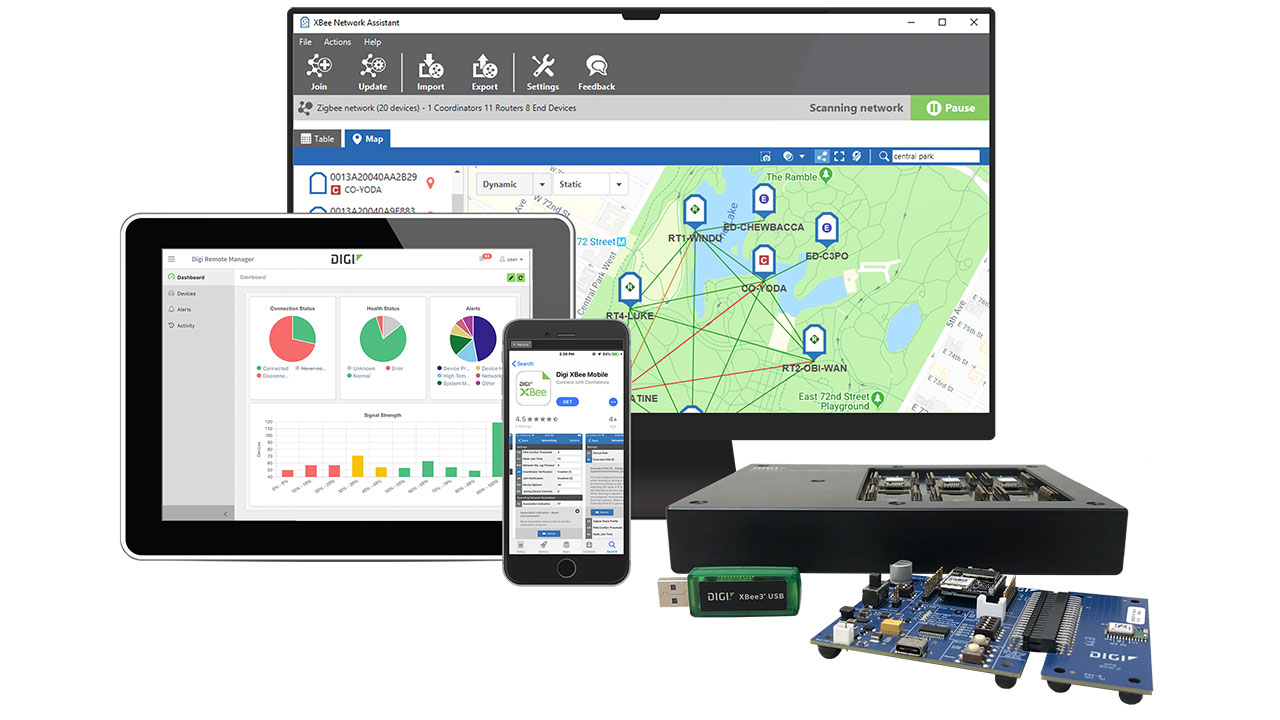 Digi XBee® modules provide flexible, low-power connectivity solutions for sensor networks and automation systems. These embedded modules support a range of options including Zigbee, DigiMesh®, Wi-Fi, Wi-SUN, Bluetooth and cellular, supporting diverse connectivity within integrated logistics operations.
Digi XBee® modules provide flexible, low-power connectivity solutions for sensor networks and automation systems. These embedded modules support a range of options including Zigbee, DigiMesh®, Wi-Fi, Wi-SUN, Bluetooth and cellular, supporting diverse connectivity within integrated logistics operations.
Mesh networking extends coverage and improves reliability, while low power consumption extends battery life for remote sensors. the complete XBee ecosystem includes a full developer tool suite, Digi XBee Tools, which include tools for provisioning, testing and monitoring XBee networks, and enabling cost-effective IoT deployments for inventory tracking, environmental monitoring, and asset management applications.
Digi ConnectCore Development Platform for Manufacturers
The Digi ConnectCore® family of embedded solutions includes the Digi ConnectCore system-on-modules (SOMs), as well as developer tools, developer kits for rapid prototyping and testing, Digi ConnectCore Cloud Services for remote monitoring and management of deployed devices, and Digi ConnectCore Security Services, which are services and tools that enable you to maintain the security of your devices throughout the entire product lifecycle.

IoT Logistics Monitoring and Management with Digi
The transformation of modern logistics through IoT in logistics represents a fundamental shift toward intelligent, connected supply chains that deliver unprecedented visibility, efficiency, and operational excellence. Internet of Things and logistics integration addresses critical industry challenges while enabling new levels of performance and customer satisfaction. From real-time monitoring to predictive maintenance and warehouse automation, IoT logistics solutions provide competitive advantage in today's demanding marketplace.
The benefits of IoT in supply chain operations extend beyond cost reduction, encompassing improved safety, enhanced sustainability, and superior customer experiences that define industry leadership. Organizations ready to embrace this transformation can accelerate their journey by exploring comprehensive IoT solutions and discover advanced remote management capabilities.

IoT in Logistics FAQ
What business problems does IoT solve for logistics?
Logistics IoT is all about reducing costs and waste, improving efficiency and visibility, and ensuring assets and vehicles are tracked and managed, end to end. Some of the specific challenges IoT in logistics can help solve include:
- Missed ETAs and poor shipment visibility
- Temperature excursions in cold chain
- Loss/theft and misplacements of high‑value assets
- Excess yard/warehouse dwell time and detention fees
- Under‑utilized returnable transport items (RTIs: totes, pallets, kegs)
- Paper‑heavy audits and compliance gaps
What are the most common use cases for IoT in logistics?
Some of the key applications for IoT in logistics include asset and inventory monitoring, location tracking, process automation, and integration with business systems for visibility and reporting. Additionally, the ability to remotely manage devices that perform various tasks, such as automation or routing sensor data, is critical to ensure devices are running as expected and have updated firmware and security.
The following are examples of applications under the category of asset tracking and management:
- Shipment tracking: Location and condition (temp/humidity/shock/light)
- Fleet telematics: Engine, fuel, driver behavior, ELD compliance
- Yard/warehouse RTLS (Real Time Location Systems): Forklifts, pallets, dock doors, gates
- Cold chain monitoring: Pharmaceuticals, food, chemicals
- Returnable asset tracking: Pallets, containers, roll cages
- Facility monitoring: Doors, power, vibration, leaks, site security
What sensors are typically used in logistics?
Logistics applications utilize a range of sensors to monitor and report on location and conditions. These include GPS/GNSS, temperature, humidity, accelerometer/shock, light (door open), tilt, pressure, proximity (magnetic/reed), CO₂/TVOC (specialized), and fuel/reefer controller interfaces.
How do I track asset location indoors vs. outdoors with IoT technology?
There are a number of technologies at work in indoor and outdoor asset location tracking. Here are some examples:
- Outdoors: GPS/GNSS + cellular/satellite backhaul
- Indoors: BLE beacons, UWB anchors, Wi‑Fi fingerprinting, or passive/active RFID
- At boundaries: Geofences (yard, port, cross‑dock) trigger events like “arrived,” “departed”
How long do batteries last in IoT devices used for logistics monitoring?
Battery life in deployed devices depends on reporting interval, network type, temperature, and coverage quality. Expect weeks to months for high‑frequency shipment trackers, and 1–5 years for lower‑duty asset tags. There are several important ways to extend battery life. These include reducing report frequency, using event‑driven transmission (e.g., only on movement/threshold), and choosing low‑power devices and networks like Digi XBee® and Digi X-ON®, which is based on LoRaWAN®.
What are the most advantageous networks and protocols for IoT in supply chain?
The following table provides a range of connectivity protocols for different scenarios found in logistics applications and the reason those options work well in those use cases.
| Scenario |
Typical Choice |
Why |
| Cross-border, mixed coverage |
Cellular (LTE-M/NB-IoT, 4G/5G) |
Ubiquity, mobility, decent power profile |
| Remote/out at sea |
Satellite IoT/hybrid |
Coverage where cellular fails |
| Dense warehouse/yard |
Bluetooth LE + on-site gateways or LoRaWAN® |
Lower power, higher accuracy indoors |
| Regional, low data |
LoRaWAN/private LPWAN |
Very low power + private control |
| Door sensors/short range |
Bluetooth LE, Zigbee, DigiMesh® |
Ultra-low power peripherals |
Digi supports a range of protocols, from 5G and 4G LTE cellular connectivity in our networking solutions to Cat 1, Cat 4, LTE-M/NB-IoT, Zigbee, DigiMesh, 802.15.4, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Wi-SUN and LoRaWAN in our embedded solutions.
Edge vs. cloud — what should run where in logistics applications?
The answer to the question of edge computing vs. cloud computing depends upon many different factors, including the amount of data that needs to be transferred, as well as the frequency. Here are some examples of various use cases for both edge and cloud computing:
- Edge: Filtering/aggregation, geofence checks, simple rules, store‑and‑forward for connectivity gaps
- Cloud: Long‑term storage, analytics/ML, fleet optimization, integrations, dashboards
Need more help? Digi experts in our sales and Digi Professional Services teams support organizations in making informed choices every day. Contact us for assistance.
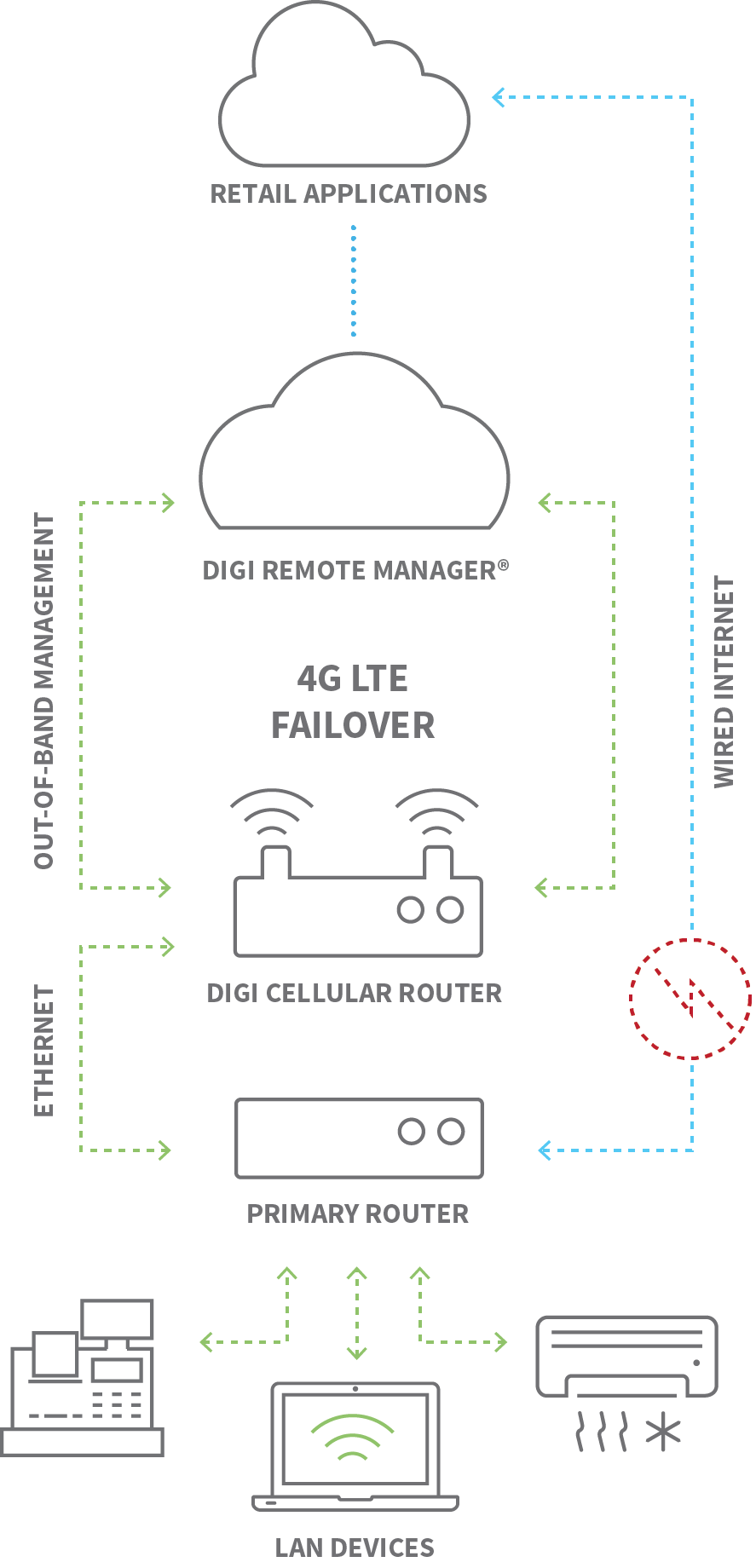
How does IoT data flow into my systems?
The typical data flow is from deployed sensors and devices to a gateway or cellular router, then to an IoT management platform that manages events and data visualization and/or routes data to business apps via APIs or webhooks.
The following is an example application diagram.
What KPIs should we track when building our IoT system?
The key performance indicator metrics for IoT in logistics depend upon your specific logistics application and requirements. Here are some examples:
- Visibility/service: OTIF, ETA accuracy, dwell time, stops per route
- Quality: Temperature/shock excursions, spoilage/returns rate
- Utilization: Asset turn rate, empty miles, RTI cycle time
- Cost: Detention/demurrage, expediting, claims
- Sustainability: Fuel burn, CO₂ per shipment, cold‑chain energy
If you need engineering support to design, build, certify and deploy your logistics application, Digi Wireless Design Services can help. Contact us to learn more.
How do we secure devices and data in our IoT/logistics application?
There are a number of key strategies for device security, physical security and network security, including:
- Unique per‑device credentials; certificate‑based authorization where possible
- TLS in transit, encrypted storage at rest
- Signed firmware + secure boot; secure OTA (over the air) updates
- IMEI/ICCID allowlisting, private APNs/APs, network segmentation (no flat networks)
- Principle of least privilege for APIs and dashboards; audit logs and alerts
- Locked cabinets and security cameras for physical security
Which regulations matter in IoT logistics applications?
Compliance with regulations in logistics applications depends on cargo, region, and phase of the supply chain. Required compliance can include pharmaceutical safety practices, food temperature rules, electronic recordkeeping, and general privacy laws. Treat compliance as a system property. For example, use defined monitoring and recording practices to ensure time‑stamped data integrity, employ strict access controls, and run auditable reports.
Meet SmartSense by Digi, delivering industry-leading cold chain monitoring and compliance solutions.
How should we pilot an IoT project for our logistics operation?
The following is a getting started checklist for piloting an IoT initiative in logistics:
- Start small, i.e. with a contained asset pool
- Define 3–5 measurable KPIs and thresholds (e.g., ≤2% temp excursions)
- Prove data quality (coverage, latency, accuracy) with a soak test
- Integrate minimally (webhooks to a sandbox) before full WMS/TMS integration
- Train operators; define exception handling via playbooks
- Plan device recovery/reuse or reverse logistics
What’s the right reporting interval for IoT devices in supply chain applications?
Balance latency vs. battery/cost. Here are some typical starting points:
- In motion: Every 5–15 minutes or on significant movement
- Stationary: Heartbeat every few hours
- Event‑driven: On shock/light/door open, geofence enter/exit
Need more assistance procuring the right connectivity and planning your IoT deployment? Contact us.
How do we handle spotty coverage in our IoT in logistics application?
There are a number of options today for managing coverage challenges. For example:
Use store‑and‑forward buffers, retry with backoff, acknowledge at the application layer, and reconcile late data (out‑of‑order events).
What are the main cost buckets for IoT in supply chain?
Costs vary in IoT projects for supply chain operations depending on whether you deploy an Opex solution or a Capex solution. For example, Digi International offers both fully managed solutions (via SmartSense by Digi, and Ventus, a Digi company) that involve only operating expense (Opex), as well as self-managed solutions that involve capital expense (Capex) as well as operating costs.
For self-managed solutions, the cost buckets typically include hardware (trackers, gateways, routers), connectivity (cellular/LPWAN/satellite), a management platform subscription, integrations, installation, cyber security integration, and training/change management.
However, Digi’s self-managed networking solutions, such as its enterprise, industrial and transportation cellular routers, come with integrated security via the Digi TrustFence® security framework, as well as an integrated device management platform via Digi Remote Manager®, which enables rapid provisioning, ongoing security monitoring, and remote management. This ensures networks can scale, and devices can be managed across their entire lifecycle, without the additional cost of an add-on management system.
Contact us for additional information and to find the right solution for your needs and budgetary requirements.
How do I estimate the ROI of a supply chain IoT project?
Here is a simple template and example to help you get started projecting the return on investment for your IoT project:
- Annual benefit ≈ (reduced spoilage/claims) + (lower detention/dwell) + (asset loss reduction) + (labor saved) + (expedites avoided).
- Annual cost ≈ (hardware amortized) + (connectivity) + (platform) + (integration amortized) + (ops).
Example:
- 5,000 shipments/year, 3% spoilage at $5,000 value each → baseline loss = 5,000 × 0.03 = 150 shipments; 150 × $5,000 = $750,000.
- IoT cuts excursions by 30% → savings = $750,000 × 0.30 = $225,000.
- Costs: 2,000 trackers × $35 = $70,000 (amortized over 3 yrs ≈ $23,333/yr); connectivity $2/device/month → $2 × 2,000 × 12 = $48,000/yr; platform $20,000/yr; integration $30,000 (amortized 3 yrs ≈ $10,000/yr).
- Total annual cost ≈ $23,333 + $48,000 + $20,000 + $10,000 = $101,333.
- Net annual benefit ≈ $225,000 − $101,333 = $123,667. Payback on one‑time spend (~$100k) occurs within the first year if benefits hold.
Related resource: See our blog post, Calculating the ROI for LoRaWAN Deployments, if you are considering LoRaWAN for your implementation.
What are the hidden costs to watch out for in supply chain and logistics IoT projects?
These vary by use case, but at a high level, they may include things like international roaming, device recovery logistics, certifications for hazardous environments, and end‑of‑life e‑waste handling. Additionally, a common mistake is for operations teams to start from scratch and build their solution from the ground up, instead of working with an end-to-end solution provider like Digi that can help accelerate time-to-value with deployment ready devices, gateways, and remote management systems.
Feel free to contact us for additional information or sales support.
What’s special about cold chain IoT?
IoT cold chain solutions like SmartSense offer calibrated temperature sensors, short reporting intervals, door‑open/light events, excursion alerts with escalation, and auditable, time‑stamped reports suitable for inspections. These solutions help to provide rapid and accurate visibility and alerts and reduce human error while ensuring compliance.
What are the top rollout mistakes in logistics IoT projects?
Next Steps